What is Structural Design
Structural design is the process of creating a framework or system that can withstand applied loads and forces while maintaining its intended functionality, safety, and stability. This process involves the analysis, planning, and design of structures to ensure they can support their own weight as well as any additional loads they may experience during their lifespan.
Key aspects of structural design include:
1. Analysis:
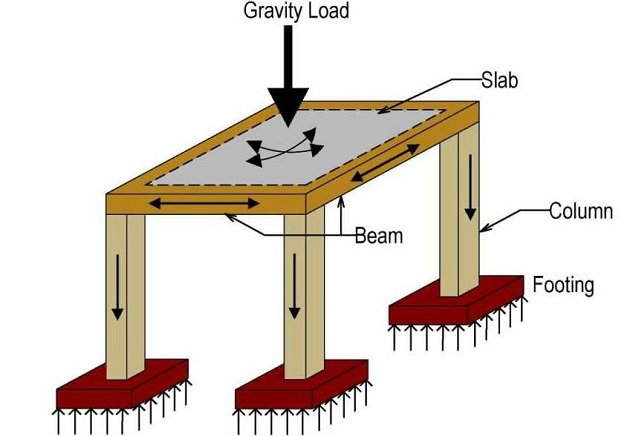
This involves evaluating the loads and forces that a structure will experience, such as gravity loads $\left(e.g., the weight of the structure itself, occupants, and contents\right)$, environmental loads $\left(e.g., wind, snow, earthquakes\right)$, and live loads $\left(e.g., people, furniture, equipment\right)$. Structural engineers use mathematical calculations, computer simulations, and modeling techniques to analyze these loads and determine their effects on the structure.
2. Material Selection:
Structural engineers must select appropriate materials for the construction of the structure based on factors such as strength, durability, cost, and environmental considerations. Common structural materials include concrete, steel, wood, and masonry. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the project.
3. Design Criteria:
Structural design must adhere to various codes, standards, and regulations to ensure the safety, reliability, and integrity of the structure. These criteria may include building codes, zoning regulations, seismic design codes, and environmental guidelines. Structural engineers must consider these requirements when designing the structure to ensure compliance and minimize risks.
4. Structural Elements:
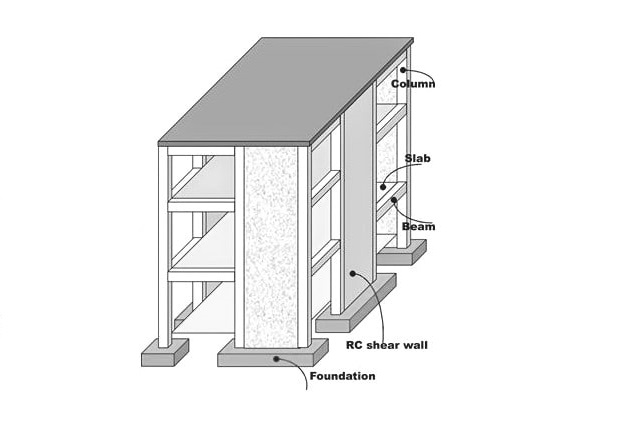
Structural design involves determining the layout, size, and configuration of structural elements such as beams, columns, slabs, walls, and foundations. These elements are designed to resist applied loads and provide support and stability to the structure. The design of these elements considers factors such as material properties, geometry, load distribution, and structural connections.
5. Load Paths:
Structural engineers establish load paths within the structure to ensure that loads are transferred safely and efficiently from the point of application to the foundation and ultimately to the ground. Load paths are designed to minimize stress concentrations, prevent structural failures, and optimize the performance of the structure under various loading conditions.
6. Structural Systems:
Structural design involves selecting and designing appropriate structural systems for the intended use and function of the building. Common structural systems include frame systems, shear wall systems, truss systems, and hybrid systems. The choice of structural system depends on factors such as building height, architectural requirements, and site conditions.
7. Safety Factors:
Structural engineers apply safety factors or margins of safety to account for uncertainties, variability, and unforeseen conditions in the design process. Safety factors ensure that the structure has sufficient strength and stability to withstand loads and forces beyond those considered in the design calculations.
Overall, structural design is a critical aspect of the construction process, ensuring that buildings and other structures are safe, functional, and durable throughout their intended lifespan. It requires a thorough understanding of structural mechanics, materials science, building codes, and engineering principles to create successful and efficient designs.