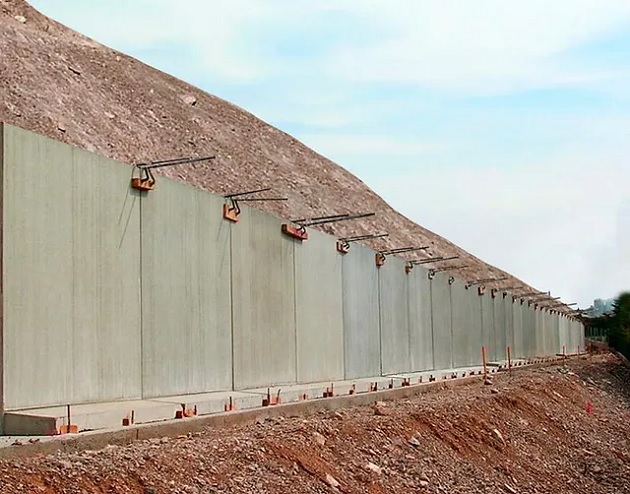
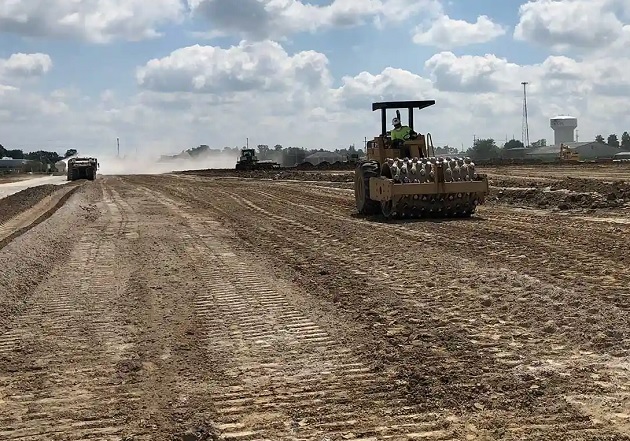
Geogrid in roadways
Geogrids play a crucial role in roadway construction and reinforcement. These are materials made of polymers or other durable materials formed into a grid-like structure. They’re used primarily for soil reinforcement and stabilization in roadway construction. Here’s how they’re utilized:
-
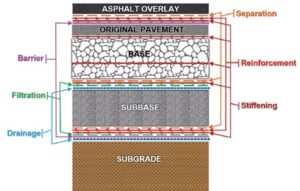
Soil Reinforcement: Geogrids are placed within or beneath the layers of soil or aggregate used in road construction. They act as a reinforcement layer, distributing loads more effectively and reducing the potential for soil movement or deformation under traffic.
-
Improving Load Distribution: By adding geogrids, the load distribution characteristics of the roadbed are improved. This helps prevent rutting, cracking, and other forms of pavement distress, extending the road’s lifespan.
-
Stabilizing Slopes and Embankments: Geogrids are also used to stabilize slopes and embankments along roadways. They reinforce the soil, preventing erosion and slippage, which can compromise the stability of the road.
-
Reducing Construction Costs: Geogrids can sometimes allow for the use of locally available or lower-quality fill materials, reducing the need for high-quality, expensive fill. This can lead to cost savings in construction.
-
Enhancing Performance in Soft Soils: In areas with soft or weak soils, geogrids help to improve the load-bearing capacity of the subgrade, making it more suitable for constructing roads.
Overall, geogrids significantly contribute to the structural integrity and longevity of roadways by improving soil stability, load distribution, and reducing maintenance needs, especially in areas prone to soil movement or poor soil conditions.

